| Using XMLink Universal Gateway |     |
XMLink Universal Gateway provides Oracle Tuxedo applications access to services deployed on other Enterprise Information Systems (EISs).
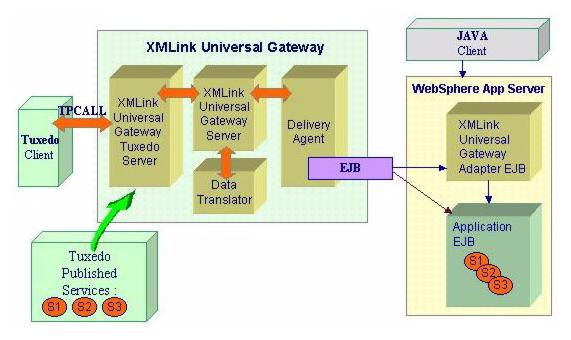
Figure 2-1 XMLink Universal Gateway Components
The Tuxedo Client |  |
With XMLink Universal Gateway, the Tuxedo client makes service calls in the usual manner using tpcall to call services. XMLink Universal Gateway does not require anything to be installed on Tuxedo clients.
After you enhance your Tuxedo applications to call new enterprise services, you only need to configure the XMLink Universal Gateway Tuxedo server to advertise those services for your Tuxedo clients.
XMLink Universal Gateway |  |
XMLink Universal Gateway has the following components on the Tuxedo server machine:
The XMLink Universal Gateway Tuxedo server shares with other Tuxedo servers its ability to advertise services to Tuxedo clients, but instead of executing the business logic itself, the Gateway Tuxedo server interacts with the EIS to execute its service calls. Using its GATEWAY_SERVICE, it advertises the availability of enterprise services and funnels those requests to the appropriate system.
The Enterprise Information System |  |
The Enterprise Information System (EIS) contains:
The EIS is generally a J2EE application server, such as IBM WebSphere.
Irrespective of the delivery agent used, you will need to build and deploy services in your enterprise applications. These services can be Java classes, EJBs, COM components, Web services, or other implementations of business logic.
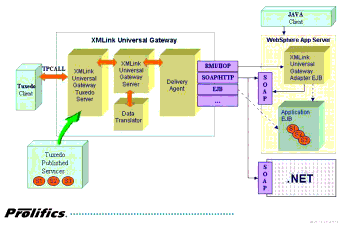
For the SOAP-RPC delivery agent, you need an HTTP server that is configured to process SOAP requests.
For the RMI/IIOP delivery agent, typically the J2EE application server is configured to process RMI/IIOP requests. You also need to install the XMLink Universal Gateway Adapter EJB which processes the RMI/IIOP requests, forwarding them to the SOAP layer.
For the EJB delivery agent, XMLink Universal Gateway can interact directly with the EJBs containing the business logic, without using SOAP, Web services, or the Gateway Adapter EJB.
Alternatively, the Gateway Adapter EJB can also be used in the configuration.
Accessing Enterprise Services
Using SOAP-RPC
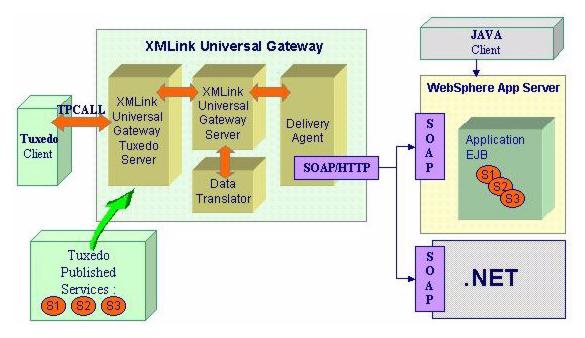
Using RMI/IIOP
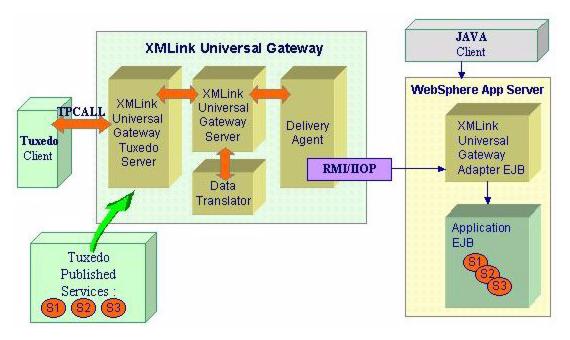
Using EJB